
Biometric Land Registration
GABS Biometric land registration solution refers to the use of biometric technology to uniquely identify individuals participating in land registration processes. Normally traditional land registration systems often involve paper-based documentation, which can be time-consuming and susceptible to fraud. Integrating GABS biometric solution, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans, adds a layer of security, accuracy, and efficiency to the land registration process.
Biometric Enrollment
- Individuals involved in land registration undergo biometric enrollment, where their unique biological characteristics are captured and stored in a database.
- Common biometric modalities include fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns, and sometimes palm prints.
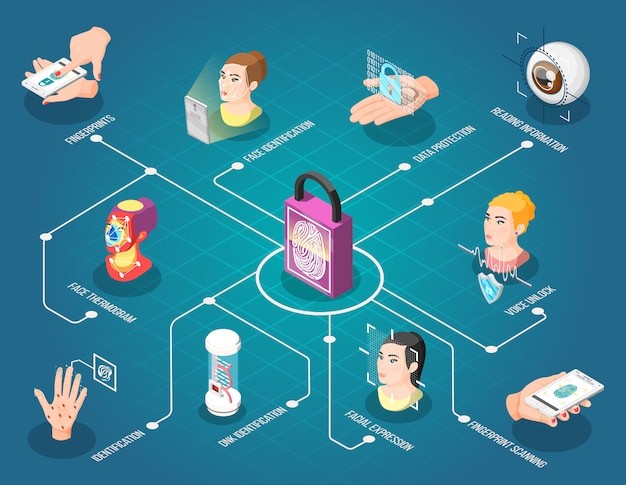

Identity Verification
- During land transactions or registration processes, individuals can be verified using their biometric data.
- Biometric scanners are used to match the presented biometric information with the stored data to confirm the identity of the person involved.
- Biometric data is difficult to forge or replicate, adding a high level of security to the land registration process.
- This helps prevent identity theft, fraudulent transactions, and unauthorized access to land-related records.

Integration with Land Information Systems
- Biometric land registration systems are fully integrated with existing land information systems to create a comprehensive and secure land registry.
- Integration facilitates easy access to accurate and up-to-date land-related information.
- The biometric land registration systems are completely compliant with relevant legal and regulatory frameworks governing data privacy and biometric usage.
- Clear consent mechanisms and data protection measures are taken into consideration with highly secured technical components.
Efficiency and Accuracy
- Biometric technology streamlines the registration process by eliminating paperwork and reducing the potential for errors.
- Automated biometric matching ensures quick and accurate identification of individuals.
- Biometric land registration systems can potentially support remote authentication, allowing individuals to participate in the registration process without physically visiting a registration office.
- This can be especially useful in rural or remote areas.
